If you are reading this, you’re probably wondering “Should I use a polycarbonate enclosure or a fiberglass enclosure?” This is a very valid question to have.
Often we find companies continue to use fiberglass because they are unaware of the advantages of working with plastic enclosures; and, the inherent value in using this versatile thermal set plastic.
When it comes to the NEMA ratings, a 4X enclosure is a 4X enclosure when it leaves the factory, regardless of the material. How well the enclosure performs during its service life will determine your return on investment.
Today, polycarbonate is one of the most versatile types of plastic used in industrial applications throughout the world.
Today, polycarbonate is one of the most versatile types of plastic used in industrial applications throughout the world. Polycarbonate roofs, in particular, offer significant advantages in terms of safety, UV resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making them a superior choice for environments that require durability and long-term performance, such as educational and commercial buildings.
Material Comparison
When it comes to choosing between fiberglass and polycarbonate enclosures, it’s essential to consider the material properties of each. Fiberglass enclosures are made from a composite material consisting of glass fibers embedded in a plastic matrix. This combination provides excellent strength, durability, and resistance to extreme temperatures. On the other hand, polycarbonate enclosures are made from a versatile type of plastic that is known for its impact resistance, transparency, and ease of customization. While both materials have their strengths and weaknesses, polycarbonate enclosures are generally preferred for their superior impact resistance and lighter weight.
Impact Resistance
Polycarb can withstand an impact of over 900 psi; fiberglass comparatively can only withstand about 225 psi. As a thermal set plastic, polycarb flexes and return to its original shape, while fiberglass can shatter with on impact. This makes polycarbonate the preferred choice for applications requiring high impact resistance.
Winner: Polycarbonate
UV Resistance
When exposed to UV light for prolonged periods of time, the color of fiberglass material will fade. This process is called as photodegradation or more commonly known as “sun bleaching’ or “bleaching.”
Photodegradation occurs when ultraviolet rays break down the chemical bonds of the dyes in an object and the colors fade.
More importantly, however, fiberglass can also delaminate with prolonged UV exposure, this more commonly known as “blooming.” Delamination is when the layers of fiberglass strands and resin separate from each other or from the core sandwiched between the layers, exposing the glass fibers on the surface of the enclosure. It gives the enclosure a rough or fuzzy texture.
Delamination is a common problem and can eventually compromise the overall structural integrity of the enclosure – resulting in a system failure of the internal components. Fiberglass roofs are suitable for homes exposed to both warm and cold weather conditions, but can deteriorate under hot weather. Replacing either the enclosure or the entire unit may be required, costing time and money.
Plastic injection molded enclosures do not have layers to delaminate. Fibox uses a specially formulated plastic with UV inhibitors to withstand prolonged exposure to the sun. Polycarbonate roofs are recommended for areas with hot weather due to their UV light resistance and color retention features.
Fibox took part in a UV exposure resistance study. The results showed that although a slight “bleaching effect” may occur over time, the Fibox enclosures became more durable in the field. This result is due to a chemical reaction that the plastic has with the UV rays.
In some cases, Fibox clients have begun upgrading the internal components of their designs with a subsequent generation on-site while continuing to use their original enclosing investment. Recycling the enclosure saves time and money with a longer lasting Fibox enclosure.
Winner: Polycarbonate
Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP) vs. Polycarbonate
Glass Reinforced Plastic (GRP), also known as fiberglass, is a composite material that consists of glass fibers embedded in a plastic matrix. While GRP is a strong and durable material, it has some limitations when compared to polycarbonate. For instance, GRP is more prone to damage from UV rays, which can cause the material to degrade over time. Additionally, GRP is more difficult to modify and customize than polycarbonate, which can be easily cut, drilled, and shaped to meet specific requirements. In contrast, polycarbonate is a more versatile material that offers excellent impact resistance, transparency, and ease of customization.
Modifications
A stock enclosure does not remain stock for long. At some point, an engineer or technician will alter the box with holes, cutouts, and recesses. These changes are necessary to make the enclosures functional. Fiberglass and polycarb respond differently to such modifications.
Fiberglass is comprised of layers of resin and glass fibers. When cut, drilled, or otherwise modified, it can splinter like wood, resulting in a rough, chipped edge (image 1).
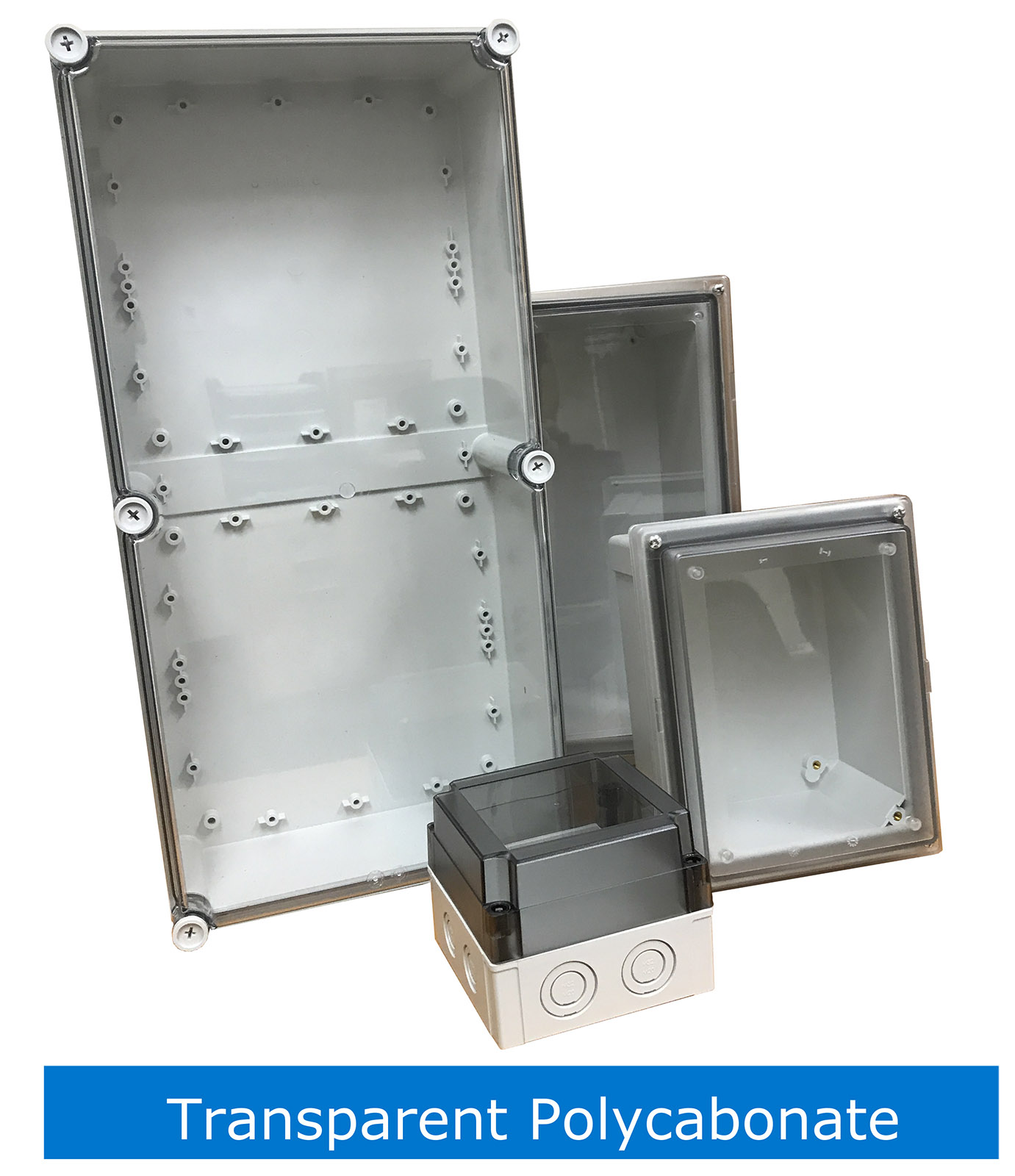
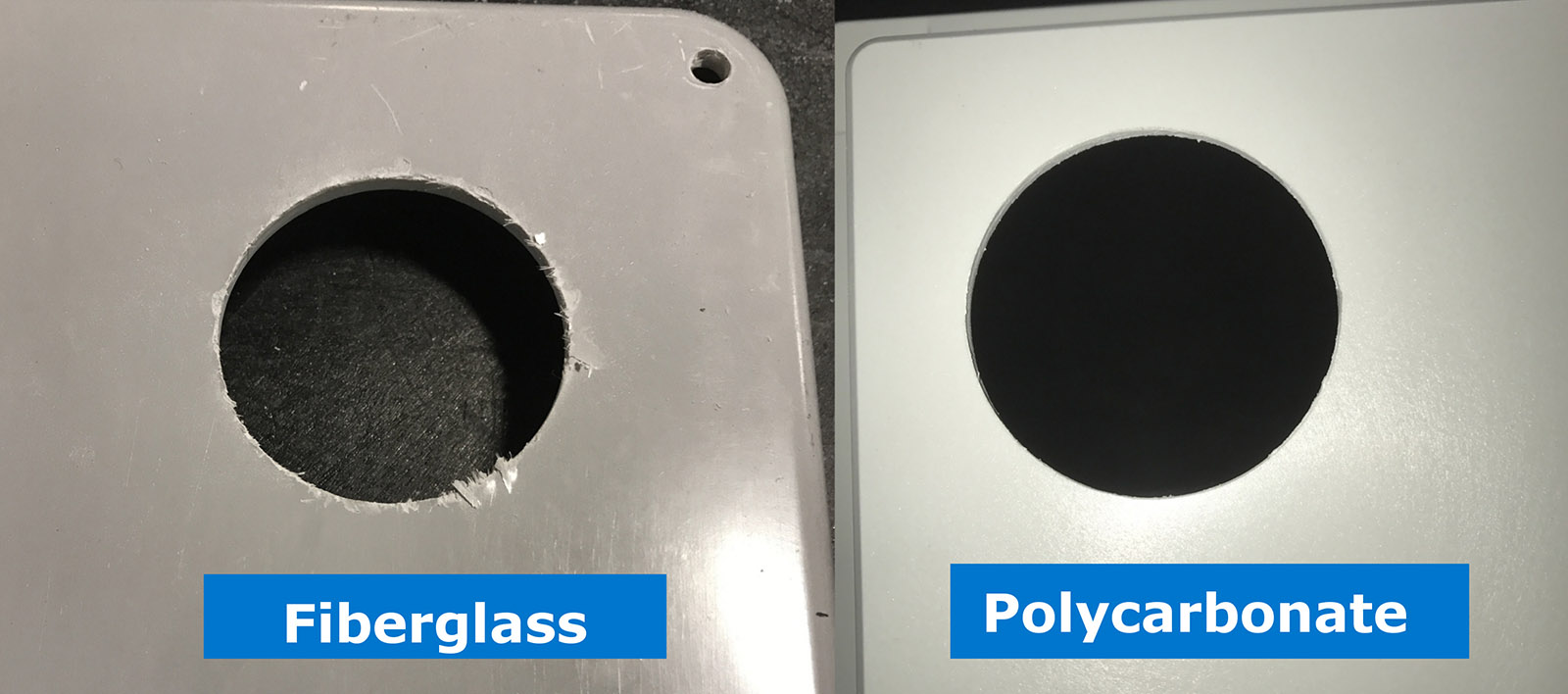

Moreover, the cutting process produces a dust containing glass particles. This dust can irritate the eyes and any exposed skin. Inhaling the dust can impact respiratory function. Handling fiberglass modifications require the user to “suit up” to ensure safety. Conversely, modifying polycarbonate produces larger specks of material that are too heavy to become airborne. These specks will not irritate the skin and can be easily swept up or vacuumed. Additionally, if a transparent cover is required, this is easily accomplished with a polycarbonate enclosure. Fibox offers many transparent cover options and can easily install a transparent cover. (Image 2).
In contrast, polycarbonate is a more versatile material that offers excellent impact resistance, transparency, and ease of customization. Polycarbonate roofs provide superior safety, UV resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making them an ideal choice for environments requiring durability and long-term performance, such as educational and commercial buildings.
Winner: Polycarbonate
Weight
Fiberglass outweighs plastics by varying amounts. Fiberglass enclosures have thicker walls than a plastic enclosure. For example, a 16x14x8 Fibox enclosure weighs 7.3 pounds. Compare that to a smaller sized, 16x14x6 fiberglass enclosure which weighs 8.9 pounds.
The costs associated with greater weight can go well beyond the initial shipping costs from the supplier’s warehouse until the unit arrives at its final destination. Shipping costs can quickly increase the overall product cost – not to mention the additional strain on human resources when carrying heavier enclosures.
These costs are magnified when working with larger sized boxes. Using a polycarb enclosure will save money on shipping and human resources right off the bat. Polycarbonate is the preferred choice for applications requiring clear visibility and design flexibility.
Winner: Polycarbonate
Cost
Polycarbonate and fiberglass are comparably priced, however, with all the factors stated above fiberglass can cost you and your company more in time and money. These possible cost drivers include shipping, potential redoing modifications and a shorter, less reliable field life.
Winner: Polycarbonate
Environmental Factors
When choosing between fiberglass and polycarbonate enclosures, it’s essential to consider the environmental factors that may affect the material’s performance. For instance, extreme temperatures, UV rays, and exposure to chemicals can all impact the material’s structural integrity and service life. Polycarbonate enclosures are generally more resistant to environmental factors than fiberglass enclosures, thanks to their excellent impact resistance and UV stability. However, both materials can be affected by extreme temperatures, and it’s essential to choose the right material for the specific application.
